By Paul R Salmon FCILT FSCM FCMI
Introduction
From ration packs to repairables, military logistics involves moving millions of items across a complex and high-stakes network. In an environment where readiness can’t wait, anything that improves visibility, traceability, and speed is worth attention. One of the simplest – yet most overlooked – technologies making a quiet revolution in logistics is the humble QR code.
Originally developed for the automotive industry in the 1990s, QR (Quick Response) codes have found new relevance in the defence supply chain. Their ability to store and transfer data quickly using just a smartphone or handheld scanner makes them a compelling tool for military logistics, especially when paired with evolving digital enablers like Electronic Technical Instructions (ETIs), asset management platforms, and mobile warehousing systems.
This article explores how QR codes are being used across defence logistics, their benefits and limitations, and how they can support smarter, more secure supply chains.
What is a QR Code – and Why Does it Matter?
A QR code is a type of two-dimensional barcode that can store much more data than a traditional linear barcode – including URLs, serial numbers, geo-locations, and structured item-level metadata.
Unlike traditional barcodes that typically hold only an identifier linked to a database, QR codes can embed operationally useful information directly in the image – making them particularly useful in austere or disconnected environments.
In defence logistics, this is more than a convenience: it’s a capability enabler.
How QR Codes Are Being Used in Defence
1. Item Identification and Traceability
QR codes can store detailed item metadata, such as:
NATO Stock Number (NSN) Batch number Serial number Maintenance schedule Origin and supply route Usage instructions (linked via URL)
This enables precise, in-field scanning for inventory and asset management. No more scribbled tags or verbal handovers – a scan gives the warfighter instant access to the right information.
2. Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
In a Condition-Based Maintenance regime, each item can carry a unique QR code that links to its current health status or service record. This allows:
Instant check of servicing status Integration with predictive maintenance tools On-the-spot update to maintenance logs
QR codes can bridge the gap between paper-based logs and live digital systems, even in bandwidth-constrained environments.
3. Electronic Technical Instructions (ETIs)
QR codes on equipment can link directly to technical manuals, safety notices, or video instructions. This ensures:
The latest version is always accessed Human error is reduced Training and field support are improved
In an environment where configuration control is paramount, this helps ensure compliance without carrying heavy manuals or relying on memory.
4. Warehouse Management and Inventory Audits
QR codes improve speed and accuracy in stores functions. Benefits include:
Faster picking and put-away Reduced mis-identification Live stock updates via handheld devices
Combined with warehouse automation systems and Integrated Logistics Support (ILS) tools, QR codes help create an accurate, up-to-date picture of materiel holdings.
5. Supply Chain Security and Counterfeit Prevention
Each QR code can act as a digital signature or verification token, validating the authenticity of parts. This is especially important for:
High-value or safety-critical items Additive manufactured spares Parts sourced from complex international supply chains
QR codes, when paired with blockchain or encrypted provenance tracking, can help prevent counterfeit infiltration and improve assurance across the chain.
Advantages in the Defence Context
📦 Low-Cost, High-Impact
QR codes are easy to generate, print, and scan. They require minimal infrastructure and can be applied retroactively to existing stock.
🔐 Supports Security and Accountability
By encoding individual item-level identifiers, QR codes support detailed audit trails – useful in cases of loss, theft, or post-incident reviews.
📲 Field-Ready
Modern smartphones and tablets, increasingly deployed with field units, come equipped with QR scanners. This makes adoption fast and intuitive – even in austere environments.
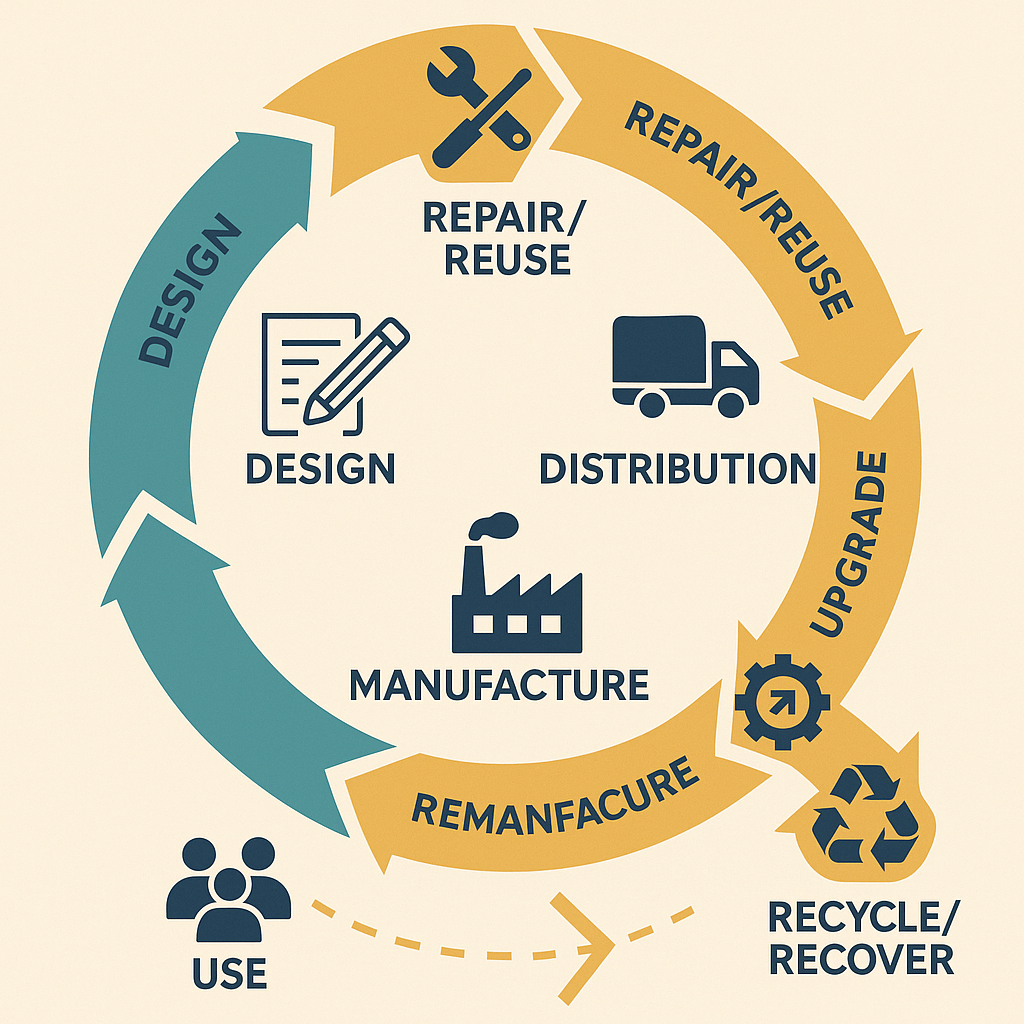
🔁 Enabler for Closed-Loop Logistics
With real-time scan feedback, QR codes can support closed-loop tracking of items, containers, and returnable packaging – a key feature in sustainable logistics models.
Challenges and Considerations
🖨️ Durability in Harsh Environments
QR codes must be printed or etched in a way that survives dirt, abrasion, oil, salt, and rough handling. Labels may need to be ruggedised or embedded in the material itself.
🔌 Connectivity Limitations
If a QR code simply points to an online resource, it may be useless in disconnected or low-bandwidth environments. Embedding critical data directly into the code, or ensuring offline content caching, is essential.
🔍 Data Overload vs Utility
While QR codes can store large volumes of data, more isn’t always better. Carefully curating the data ensures quick scans and operational relevance.
🔐 Security Risk of Open Links
QR codes can be spoofed like any data source. Defence systems must use secure QR implementations – such as codes signed by trusted authorities or scanned within secure apps.
QR Codes in Action: Use Cases Across Defence
🚁 Forward Repair Bases
QR codes on toolkits and Line Replaceable Units (LRUs) reduce the time needed to issue, identify, and return parts – enabling faster equipment turnaround.
🚚 Tactical Resupply Packages
Pallets and containers with QR-coded contents lists can speed up unloading, simplify manifests, and improve confidence during handovers in-theatre.
🧰 Expeditionary Maintenance Teams
Engineers scanning a QR code on-site can immediately pull up schematics or view previous fault history, enabling better-informed fault diagnosis.
🔁 Reverse Logistics
QR tags on returnable packaging or recoverable spares can facilitate tracking, reducing loss and improving cost recovery.
Future Potential
The real power of QR codes lies not in the code itself, but in how it connects the physical world to the digital thread.
Looking ahead, we can expect:
Integration with Digital Twins: A scanned item links to a live model of its usage, degradation, and remaining life. AI-Supported Maintenance: QR code history feeds into machine learning algorithms to predict failures. Smart Packaging: Dynamic QR codes that update status based on temperature, tampering, or movement.
In combination with blockchain, secure mobile apps, and augmented reality, QR codes can anchor trust, speed, and transparency in the defence supply chain.
Conclusion: Small Code, Strategic Impact
In a world of hypersonic missiles and AI-enabled decision-making, it’s easy to overlook the role of a black-and-white square printed on a label. But make no mistake: QR codes are quietly transforming how we manage assets, track spares, and deliver operational readiness.
In the defence supply chain, where assurance, speed, and auditability are mission-critical, QR codes offer a rare combination of simplicity, affordability, and impact.
They’re not just about better barcoding. They’re about smarter logistics.
About the Author
Paul R Salmon FCILT FSCM FCMI is Chair of the CILT Defence Forum and a lead voice in defence supply chain innovation. With a background in engineering and logistics across the MOD, Paul champions the application of digital enablers to improve availability, resilience, and readiness.





Leave a Reply